Key Message
The report identifies a critical need for increased investment in urban Nature-based Solutions (NbS) to address climate resilience and urban sustainability. Despite significant global funding for NbS, urban-specific investments remain underfunded, representing less than 5% of the estimated need. Successful case studies from Melbourne, Freetown, and Monterrey, among others, demonstrate the potential of urban NbS to provide multiple benefits, including enhanced biodiversity, climate mitigation, and socio-economic improvements. To bridge the funding gap, the report calls for a comprehensive database to track urban NbS investments, enhanced advocacy for NbS integration in urban development, and stronger alignment of national and subnational strategies. Collaborative efforts among public, private, and philanthropic sectors are essential to scale up successful initiatives and build resilient, sustainable urban environments that can withstand future climate impacts.
Summary of Key Findings
- Urban Nature-based Solutions (urban NbS) categories are absent from comprehensive global NbS funding accounts. While UNEP’s 2022 State of Finance for Nature (2022 SFN) is pacesetting, outlining $154 billion (US $2022) of current NbS spending and additional investment needs of 384 – 674 billion per year through 2050 ($18 trillion by 2050) it does not disaggregate or analyze urban NbS.1 Within the SFN 2022 accounting, public sector spending is dominant, with 86 percent (or $126 billion) of the total. Biodiversity constitutes nearly 40 percent (58 billion); agriculture, foresting and fishing, 18 percent (29 billion); land and natural resource management, 11 percent ($17 billion), 8.5 percent ($13 billion) for air and water pollution abatement, and 6 percent ($9 billion) for environmental policy. Such urban NbS as parks, urban agriculture and forests, and flood protection may be included in these public spending categories.
- Nonetheless, preliminary data exists and offers an indication that, like NbS generally, NbS in cities is severely underfunded. A comprehensive database documenting urban NbS is needed to estimate the actual gap. Based on the 2022 SFN report and the 2022 Green Climate Fund2 assertion that “Seventy percent of known climate solutions fall under the boundaries of subnational authorities,” a rough estimate of the needed annual funding for subnational areas could be upwards of $260 – 470 billion per year urban NbS is some fraction of this sum. The limited sources of available data reveal that funding urban Nbs and nature in cities in the past ten years adds up to less than five percent of the estimated annual subnational need.
- Moreover, funders often nest urban NbS within large infrastructure projects. Funders roll urban NbS into multi-project programs that encompass one or more city systems, into various funding programs (e.g., climate mitigation, resilience, or adaptation), or in ESG or impact investment reporting. A recent exception are multilateral development banks’, donors’, and specialized NGOs’ reports that measure NbS in their city-focused projects.
- A new conceptual paradigm that values, identifies, tracks, and evaluates urban NbS would enable public and private decision-makers to develop a holistic portfolio to address the environmental and socioeconomics impacts of climate change more effectively. According to one major funder, “one very important barrier [to investment in urban NbS] is the lack of understanding of the benefits – economic, social, as well as the scale of environmental benefits…. Cities lack data on many things and nature comes at the very end of the list.”
- Overall, this research provides a foundation for a call to action to improve data collection, to enhance advocacy, and increase funding for local projects and capacity building. Successful urban NbS show that it is possible to implement it at the local level, yet more action is needed.
1 Climate Policy Institute
2 Green Climate Fund Subnational Climate Fund description
Introduction
This paper, Assessing Nature-Based Solutions (NbS) for Urban Resilience, is the research supplement for the State of Nature for Cities, Time to Assess, a report co-authored by Penn IUR and the United Nations Environmental Programme (UNEP, 2023). It provides a preliminary examination of urban NbS including assessing available data, current programs, and needed action for its improvement. It has four parts: 1. Conceptualizing Urban NbS, 2. Financing Urban NbS, 3. Case Studies of Successful Urban NbS and 4. A Call to Action. In order to gather insights about the challenges and opportunities cities have regarding investments in urban nature, the team conducted 16 interviews with mayors, city officials, representatives from international financial institutions, private sector entities and civil society. The respondents represented individual cities from the Global North and Global South as well as those with a global view due to their positions with international organizations. They all offered valuable insights into growing investments in urban NbS.
Penn IUR and UNEP believe that counting such investments is of great interest to public and private decision-makers concerned with climate change and protecting cities, cities which house more than 4 billion people today (and the 7 billion urbanites of tomorrow) and represent 80 percent of the world GDP and 70 percent of global greenhouse gasses (GHGs)3 In fact, UNEP acknowledges that the current asset value of urban areas, estimated to be $4 trillion, calls for increasing cities’ resilience through nature-based solutions to address a range of natural disaster risks. For example, in the absence of any preventive actions, annual urban flood losses of more than $700 billion will likely occur by 2050.4
Ecosystem NbS advocates and researchers define NbS as, “actions to protect, sustainably manage, or restore natural ecosystems that address societal challenges by simultaneously providing human well-being and biodiversity benefits”, concentrating on interventions at forest, marine or agricultural spatial scales. This focus on ecosystems, although critical, neglects the urban dimensions of NbS. Long-term biodiversity and ecosystem health depends on strong, synergistic NbS relationships along an urban-rural continuum. While urban land consumption is much lower that of forests and agriculture, its ecological impacts are important, and those impacts will continue to grow – 60 percent of anticipated urbanized land by 2030 is yet to be developed and 90 percent of urban areas have vulnerable river sites or coastlines. Integrating NbS in urban land use and infrastructure decision-making is a critical element of an effective climate change portfolio, a concept that the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework Agreement (GBF) reinforced in the Declaration from the Convention of Biological Diversity (COP 15) in December 2022 when it called for nations to: 5 “Significantly increase the area and quality and connectivity of, access to, and benefits from green and blue spaces in urban and densely populated areas sustainably, by mainstreaming the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity, and ensure biodiversity-inclusive urban planning, enhancing native biodiversity, ecological connectivity and integrity, and improving human health and well-being and connection to nature and contributing to inclusive and sustainable urbanization and the provision of ecosystem functions and services.” 6
3 World Bank, April, 2020.
4 Pinko, N., et.al., June 2020, p.1; World Resources Institute, April 23, 2020, World Bank April 2020.
5 World Bank, April, 2020.
6 Target 12, Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework” (GBF)
1. Conceptualizing Urban NbS
NbS is a term first championed by the IUCN and the World Bank fifteen years ago to incorporate biodiversity and ecosystem considerations in climate mitigation and adaptation solutions. In 2022, the United Nations adopted the following definition of NbS: “Actions to protect, conserve, restore, sustainably use and manage natural or modified terrestrial, coastal, and marine ecosystems which address social, economic and environmental challenges effectively and adaptively, while simultaneously providing human well-being, ecosystem services and resilience and biodiversity benefits.”7
1.1 Definitions
Defining NbS in the urban context is a critical component of this broader mitigation and adaptation discussion because their unique characteristics and spatial scale set them apart from, yet remain connected to, conventional NbS landscape strategies.8 Urban nature-based solutions are complex and complicated but the current literature and interviewed experts and policymakers broadly agreed that urban NbS and investment in nature encompass the “principle of bringing nature into cities for the multiple benefits that it can deliver.” 9
The EU Commission defines urban NbS as “solutions that are inspired and supported by nature, which are cost-effective, simultaneously provide environmental, social and economic benefits and help build resilience. Such solutions bring more, and more diverse, nature and natural features and processes into cities, landscapes and seascapes, through locally adapted, resource-efficient and systemic interventions.”10
By comparison, The World Bank defines NbS for urban resilience as: “approaches that use nature and natural processes for delivering infrastructure, services, and integrative solutions to meet the rising challenge of urban resilience. [They] use a set of structural and non-structural interventions that protect, manage, restore, or create natural or nature based features…and can be applied across spatial scales and settings in and around cities.” 11
Although concise, definitions like these are broad, covering a wide spectrum of interventions and strategies that predate its use and are therefore often conflated together. The EU notes that the term “NbS” encompasses a range of existing labels from low impact developments (LIDs, in usage from 1977), to green infrastructure (GI, 1995), and sustainable urban drainage systems (SUDS, 2001) (Wild et.al., 2020, pp.106-109). The broad definitions and criteria for urban NbS also means that urban NbS are nested in economic and financing models to varying degrees. As climate policies and green financing evolve, urban NbS can be captured to varying degrees in movements such as net-zero economy, nature-positive economy, environmental economy, circular economies, social return on investment (SROI), impact investing, ESG Investing or Natural Capital Accounting. As these models continue to evolve a clear operation definition of urban NbS is necessary to track investments by public and private funders. Outlined in Table 1 is a first-level list of Urban NbS Practices to help in that effort.
7 United Nations Environment Assembly, 2022.
8 ICLEI 2017, UNEP, 2021,
9 UNEP, 2021; ICLEI, 2017.
10 https://research-and-innovation.ec.europa.eu/research-area/environment/…;
11 World Bank, 2021.
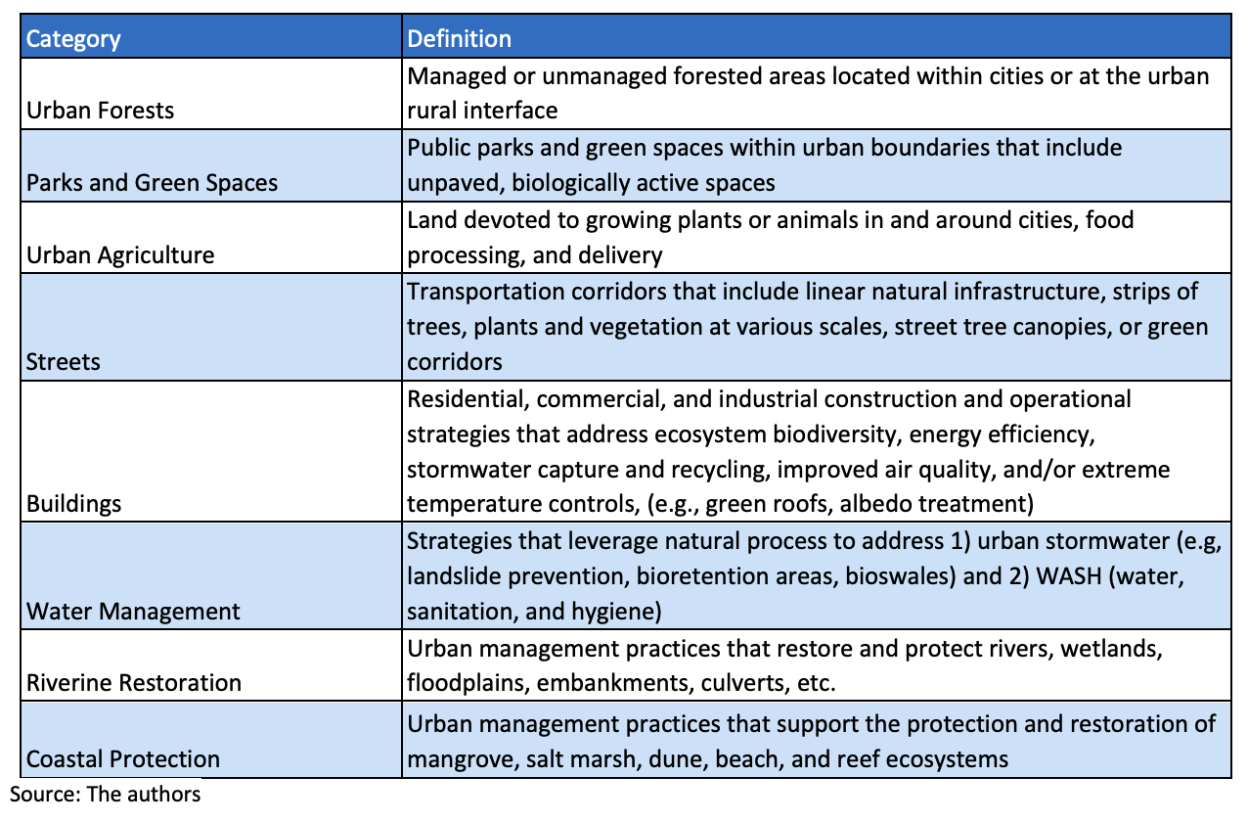
Table 1. A Taxonomy of Urban NbS Practices
It is important to note here that terminology around urban NbS such as “co-benefits”, “nature” and “natural resources” are politically and socio-culturally contested topics. The context in which urban NbS are discussed is extremely important because contested social ideas12 affect how environment and human-modified/engineered strategies are valued and therefore labeled. Confronting the value of urban NbS investmentsis forcing communities to re-evaluate and re-define their ideas of nature and well-being, even the roles and responsibilities of local government. Therefore, any global taxonomy of nature-based solutions for urban resilience or climate mitigation should be considered a political act and their measurement considered a “social process through which knowledges are gathered and produced in order to inform decision-making and wider institutional commitments.”13 Building political will and a wider institutional commitment to urban NbS practices requires a taxonomy that takes into consideration existing labels, classifications, standards and definitions.
1.2 Misperceptions about Urban NbS
There are significant challenges associated with demonstrating the business case for urban nature-based solutions. Common misperceptions come from contested concepts as well as political and governance structures and significant gap in knowledge about the cost and benefits of NbS strategies.
Little realizing the importance of investing in nature, urban leaders consider the need to invest in nature a rural, not urban, concern. Many municipal leaders don’t see the short-term political value of urban NbS and/or lack incentives to invest in nature as part of long-term adaptation strategies. In very resource-limited cities, especially in the Global South where the population in informal settlements can constitute more than 40 percent of their constituents, mayors prioritize familiar basic services strategies for housing, water, transport, open space, electricity, etc.
Without technical guidance, cities can also struggle to justify the risks of trying urban NbS. Nature-based strategies are often unfamiliar to both policymakers and those managing urban infrastructure, which makesthe benefits, risks, and costs difficult to evaluate accurately. Effectively integrating urban NbS into planning requires familiarity with the processes while operations and maintenance require new skills training. Enacting either may also require new governance mechanisms, including financial practices. Many cities are not sufficiently creditworthy to access finance, particularly for projects without a clear revenue stream, as is frequently the case with NbS-related initiatives.14
Funders interviewed for this paper generally expressed the view that in cities, "it’s much harder to demonstrate the business case [for nature-based solutions] as a sole investment, but it can be a lot easier when they’re integrated into other types of projects, like green roofs on buildings." The World Bank succinctly prescribed the desired approach as “green, when possible, gray when needed.”15
Manuel de Araujo, Mayor of Quelimane, Mozambique said of NbS in his city that, “all NbS projects have been funded with international aid, as it is not possible to do this through the municipal budget. For more than seven years almost 70% of the city’s budget was allocated to the fight against cholera; now, 50% of the budget is allocated to waste management.”
However, a growing number of mayors are embracing the climate agenda as part of their political identities, often associating it with such other issues as equitable development or environmental justice. They design and adopt municipal climate action plans incorporating nature-based projects, frequently with support from international city networks or multilateral development banks. However, given the type of goods and services provided at the urban level (transport, water, waste management, energy, housing, public spaces, etc.), most projects with a nature-based approach are nested components in larger projects dealing with resilience, mobility, stormwater management and so forth. Large infrastructure projects or regional ecosystem NbS efforts are not funded or managed by the city. This situation makes it difficult for researchers and authorities to track urban investments in nature happening in their city.
12 Osaka, Bellamy, Castree, 2021
13 Ibid.
14 According to the World Bank, fewer than 20% out of the 500 largest cities in the developing world are deemed creditworthy. The World Bank. City Creditworthiness Initiative: A Partnership to Deliver Municipal Finance https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/urbandevelopment/brief/city-creditworthiness-initiative
15 World Bank, 2021, p.15.
2. Financing Urban NbS
Globally, investments in urban NbS are at an incipient stage among public, private, and philanthropic investment entities. Funders include multilateral development banks, donor funds, specialized non-governmental organizations, governments (national to local), as well as private sector impact investors. Types of funding range from national to local government appropriations and revenues, multilateral finance institutions grants and loans, public private partnerships agreements, sales of green, blue, and impact bonds, marketing carbon offsets and such risk reducing tools as blended finance and parametric insurance (see Figure 4).
2.1 Current Financing Landscape
This section offers readers examples of the types of investment approaches offered by the three primary sources of urban NbS financing: 1) Public sector (national and local governments, multilateral banks), 2) Private sector impact investors, and 3) Philanthropic/NGO, including donor funds, multilateral grant organizations and specialized nongovernment organizations. Although developed for an article on the blue carbon market, Figure 1 (below) captures the range of sources of funding for most NbS and investments in nature. Data on these types of investments is limited. Of the sources providing information about funding for NbS in cities, some present data over more than a decade (e.g., Naturvation, an EU-focused initiative, has inventoried $800 million to $1.1 billion worth of EU urban NbS projects from 2008 to the present) while others have started tracking international program funds for just a few years (e.g., GEF’s Urban Shifts $2.1 billion).16
16 Naturvation 2017-2021; Lunjun Xie and Harriet Bulkeley, 2020; Aloke Barnwal, 2022
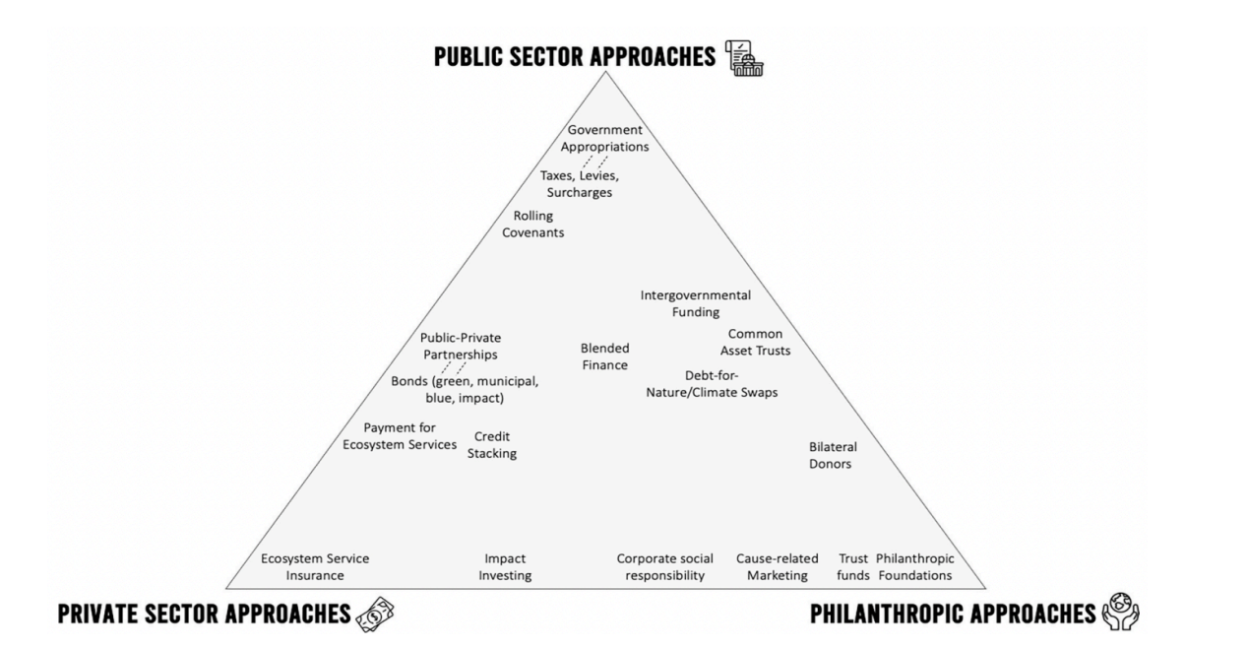
Figure 1 Summary of Sources of Funding for Urban NbS. Source: Freiss et. al., 2022
Public Funding
Global development finance institutions, whether global, regional, multilateral or bi-lateral banks, frequently focus on resilience, especially water issues, due to the ease of valuations that emphasize risk prevention and losses not incurred. They emphasize such competing development trends as the lack of basic waste and stormwater infrastructure, which leads to the degradation of urban water bodies; and informality-led urban expansion into natural resources (especially marine, forests and wetlands), which leads to loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services. 17 These realities drive institutions such as the World Bank to nest investment in nature into larger development projects. 18 Examples include their green infrastructure/stormwater management/flood control projects in urban areas that have captured some $1.5 to $2 billion in funding or the Inter-American Development Bank’s Aquafund for projects in such Latin American cities as Cuzco, Peru to build green and gray infrastructure.19
Donor funds and national and subnational governments are demonstrating a growing recognition of the importance of local action in this area. In 2020, the Green Climate Fund (GCF) created a $168 million Global Subnational Climate Fund, a fund targeted at subnational authorities to use concessional and conventional capital to leverage equity investments in climate projects ranging from $5 to $75 million, administered by Pegasus Capital Advisors.20
Despite competing development priorities and the nesting nature of urban NbS projects21 donor funds and national and subnational governments are funding city-focused programs, demonstrating the importance of local action. Singapore developed the Singapore Index on Cities’ Biodiversity (SI) in 2008 and updated it in 2021 to assist public and private sector decision-makers in formulating, financing and monitoring programs that not only promote biodiversity (e.g., native bird species) but also provide quantifiable sustainable development benefits (e.g., recreational services). Meanwhile, the EU supported a four-year project, Naturvation, that assessed more than a thousand projects primarily in cities across Europe. 22 China through its Sponge City initiative has invested between more than $12 billion in thirty pilot projects while the Netherlands in its Room for the River program has spent $2.7 billion. New York City protected its watershed with a $2.5 billion program while Toronto is currently spending $1.25 billion on its waterfront restoration effort.23
Philanthropic/NGO
Grant-giving organizations are considered catalytic investors, often coming in early before there is market or government support and providing seed money to attract other funding partners. One example is the Global Environmental Facility (GEF), which offers catalytic grants, including $310 million of grants in NbS in its Sustainable Cities program, a sum that leveraged more than $4 billion in co-financing for projects in 23 cities. 24 Specialized nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) such as the Nature Conservancy (TNC) and the World Resources Institute (WRI) fund NbS and track that funding. While neither claim to be comprehensive, each illustrates the extent and nature of funding provisions. For example, TNC has cataloged 18 Water Funds, reporting some $316 million in funding coming from local and national government and philanthropy (corporate and non-corporate). WRI’s assessment of more than 150 NbS projects that are urban or urban related (nearly 64% late stage or undergoing implementation) that have secured $100,000 or more in financing outlines how urban NbS are being effectively supported by NGOs.25
Private
Private sector investments in nature range from viable business projects, mainly in energy, to corporate philanthropy devoted to environmental and social issues. Some private sector entities engage in what is labeled “Impact investment,” a growing class of finance that in 2019 constituted an estimated $404 billion in assets (AUM).26 Defined asinvestments made with the intention to generate positive, measurable social and environmental impact alongside a financial return, they can be found across asset classes and in both emerging and developed markets. They can target a range of returns from below-market to market-rate, depending on the investors’ strategic goals.”27 Impact investors include for-profit and not-for-profit asset managers, foundations, development finance institutions (DFIs), pensions, insurance companies and others. Asset managers and DFIs represent the highest number of participants. Current records indicate that while nature is included in rating systems being developed by business associations, the metrics focus on mitigation rather than adaptation, and are concentrated in a few sectors such as food and agriculture and energy.
Other areas of private sector interest in NbS are still in the early pilot stages and/or not necessarily urban focused yet. Some are de-risking approaches based on indexed ESG efforts (e.g., HSBC World ESG Biodiversity Screened Equity UCITS ETF), blended finance (e.g., Green Climate Fund’s $250 million Global Subnational Climate Fund with Pegasus Advisors), or innovative insurance solutions (coral reef and mangrove parametric insurance in Mexico and Florida), or green bond; others provide carbon offsets through the voluntary blue carbon market (Cispata Bay, Colombia mangrove restoration/preservation).28
20 Pegasus Capital Advisors, 2020.
21 Roland White et.al., 2017, pp. 10-29.
22 L.Chan, et.al. 2021.
23 National Academy of Sciences, Medicine and Engineering, 2020.
24 Aloke Barnwal, 2022.
25 Ozment, 2021.
26 Dean Hand et. al., 2020. p.5.
27 Dean Hand, et.al., 2020, p.74.
28 HSBC, 2022; Green Climate Fund, 2022; Berg et. al., 2020; Rojan Bechauf, 2020; Daniel A. Friess, et.al., 2022
2.2 Co-Benefits - Incentivizing Urban NbS Investments
Cost-Benefit analysis (CBA) and similar valuation methods are routine mechanisms in policymaking and business. Forms of CBA are used to determine investment impacts by all four general funding sources: Public, Private, PublicPrivate Partnerships (PPP) and Philanthropic. How CBA is modeled affects investment and financing models as well as stakeholder buy-in. Assumptions can be affected by decentralization of jurisdictional control, macro-economic assumptions, political power, management, and funding from national governments, which vary significantly from country to country. CBA models do not capture all possible co-benefits or costs. A model may focus on evaluating public health or natural hazards, while leaving out factors such as biodiversity or ecosystem services. This makes arguing for urban NbS co-benefits complex.
However, CBA does provide a familiar framework for municipalities to approach NbS and evaluate investments. As a decision-making model, CBA allows urban NbS to be treated as stand-alone project elements or incorporated into larger planning and development projects and programs. Urban economists are developing instrumental CBA models that holistically evaluate the costs and benefits of urban NbS on that include the list in Table 2.
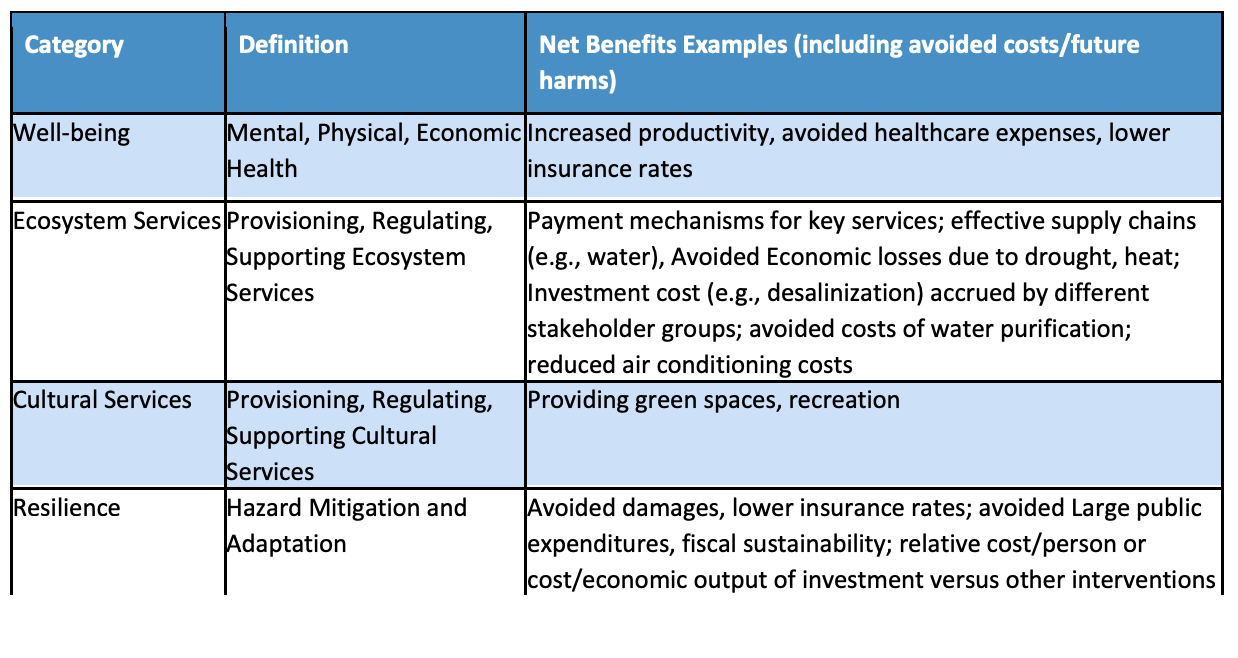
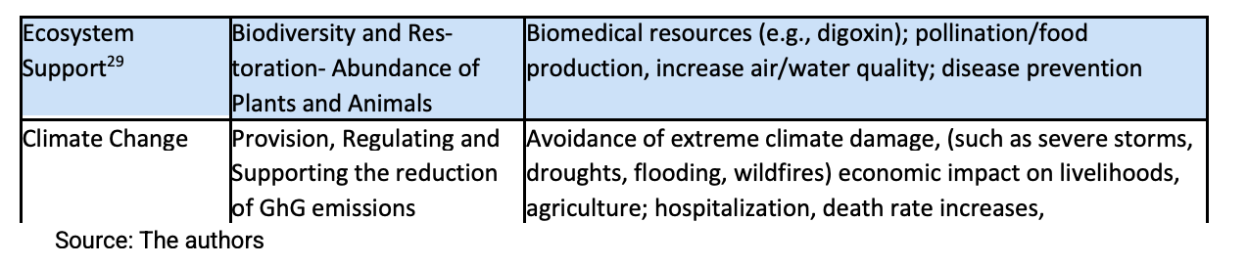
Table 2 Typology of Instrumental CBA on Urban NbS
Examples of how co-benefits are evaluated within the three funding sources include:
Private: Environment, Social and Governance Investing (ESG)
Some private sector funders engage in what is labeled “Impact investment,” or ESG, a growing class of finance that in 2019 constituted an estimated $404 billion in assets (AUM).30 Defined as “Investments made with the intention to generate positive, measurable social and environmental impact alongside a financial return, they can be across asset classes, in both emerging and developed markets, and target a range of returns from belowmarket to market-rate, depending on the investors’ strategic goals.”31 Impact investors include for profit and not for profit asset managers, foundations, development finance institutions (DFIs), pensions, insurance companies and others. Asset managers and DFIs represent the highest number of participants. Current records indicate that while nature is included in rating systems now being developed by business associations, it tends to be concentrated in a few sectors such as food and agriculture and energy and the emerging metrics tend to emphasize mitigation, not adaptation.
Public: Natural Capital Accounting (NCA)
NCA, recently adopted by the UN Statistical Commission, is an area of growing interest for cities but is not yet widely employed. Researchers originally conceived NCA to incorporate the value of natural assets in national accounts.32 They have now crafted urban natural capital accounts for several cities, including London, Belfast, Birmingham, Greater Manchester, Toronto, Vancouver, Philadelphia, and New York.33 In the United Kingdom, London and Birmingham have been active in developing local NCA. London, considered one of the world’s greenest cities yet faced with ever growing financial costs to maintain its 31,000 acres of public green area, has determined the gross asset value of its green space at more than £91 billion. This figure reflects the monetization of co- benefits related to amenities (residential property values), mental and physical health (exercise and recreation), environment (carbon sequestration, urban heat island reduction), and avoided health care costs.34 This type of accounting enabled city managers to argue successfully for increased budget allocations to support London’s green space.35 See Figure 2. Birmingham used NCA analysis to inform its 25-year Natural Capital Plan and to develop a tool used to assess the effects of new development on ten ecosystem services.36
NCA can reframe cities' approach towards investing in the environment by demonstrating the value of urban natural assets and allowing the quantification of the benefits of biodiversity and nature.37 NCA, though still in its early days for cities, has the potential to become a useful tool to build business cases for NbS projects in urban areas.
29 Pearce, 2021.
30 Dean Hand et. al., 2020. p.5.
31 Dean Hand, et.al., 2020, p.74.
32 NCAVES and MAIA (2022).
33 World Bank, 2019.
34 National Trust and Heritage Lottery Fund, 2017, pp.11, 18.
35 World Bank, 2019.
36 Holzinger and Grayson, 2019.
37 University of Liverpool, 2022.
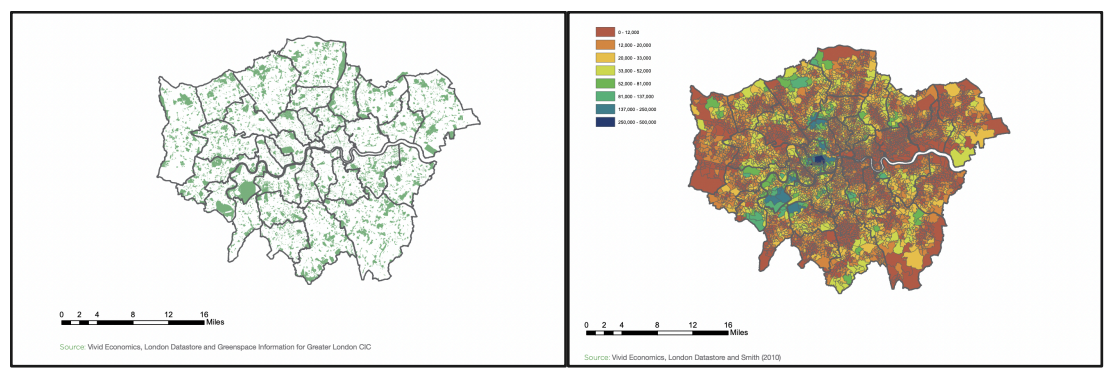
Figure 2. Greater London Public Green Areas and their Amenity Value. Vivid Economics developed a natural capital value assessment of Greater London’s Public Green Areas based on property value, health, and environmental benefits. Source: National Trust and Lottery Fund, 2017.Source: OECD, 2019; CAVES, 2022
3. Catalytic Investing: Global Environment Facility’s “True Value Methodology”
Some organizations –private, philanthropic, and public - are referred to as impact investors or catalytic capital because the funders are focused on bridging risks across a project’s financing, to increase bankability, and to help catalyze major economic transitions such as green energy. An example of public donor catalytic investing is The Global Environment Facility (GEF), a multilateral funder that provides financing and grants dedicated to “confronting biodiversity loss, climate change, pollution, and strains on land and ocean health” through “grants, blended financing, and policy support”. It is on the leading edge of Conservation Finance, an incipient effort to direct funding for Nature-based Solutions that preserve biodiversity and protect ecosystems. GEF’s sustainable cities program, now transformed into the Urban Shift partnership, takes a holistic approach to catalyzing urban sustainability, including innovative grants and financing mechanisms that combine urban development and ecosystem priorities.
One of GEF’s key innovations is blended finance to support enabling environments and mobilize private capital. According to the Convergence Network, blended finance has helped mobilize $160 Billion in financing. The G7, G20, OECD and other multi-laterals have recognized the value of blended finance to balance the “impact risk” of investments such as nature-based solutions and unlock their potential. GEF uses a proprietary approach called True Value methodology to assess the costs and benefits of proposed projects. The methodology focuses on shared value creation through identifying and expanding the connections between societal and economic progress, profits, cost reduction, and competitiveness enhancement.
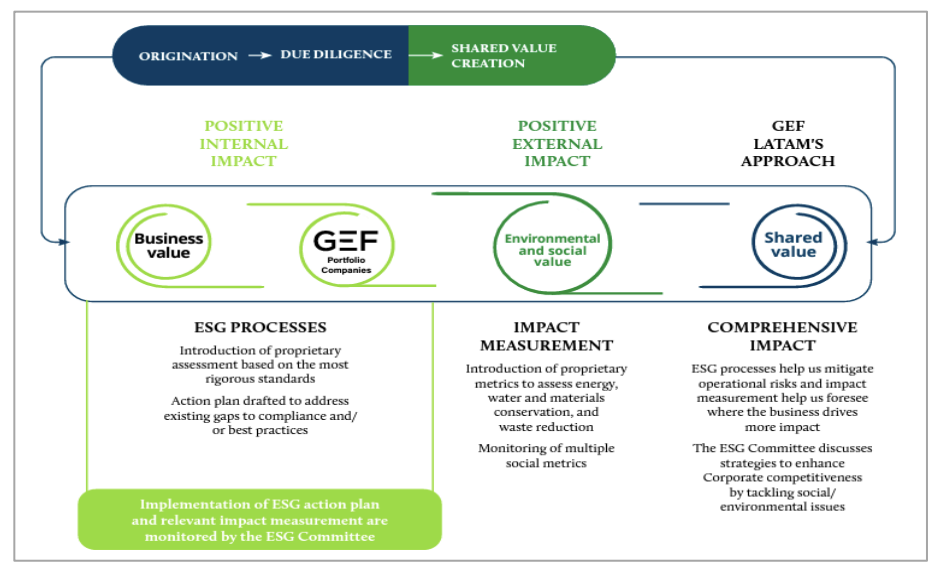
Figure 3 GET True Value Methodology, from the 2021 GEF LaTam Impact Report
2.3 The Data Gap
Quantifying all the sources for NbS funding would rely on a comprehensive database that does not yet exist as well as extensive efforts among funders or cities to disaggregate or source new data. Existing international databases offer only partial views or glimpses into the total urban NbS picture because they do not collect project or investment data that can be disaggregated at the urban scale and/or capture urban NbS benefits. Additionally, small scale NbS investments at the urban scale are part of national or subnational budgets 38 and are not reflected in global investment databases, significantly limiting accurate international estimates. While taken together, these glimpses add up to a range of $20-23 billion invested in the past decade; this figure is less than 5 percent of the needed NbS investment, roughly estimated to be $375 billion per year.39
Filling the gaps and tracking Urban NbS investment data will require partnerships to establish data standards across public, private and philanthropic sectors to support NbS in urban decision-making. Current NbS models depend on data drawn from rural areas, national coastlines and riverine valleys, forests, and agriculture that frequently do not account for urban activities. NbS investments at the urban scale that might be integrated into national or subnational budgets are not reflected in global investment databases. Existing international databases offer only partial views or glimpses into urban NbS because they, too, do not collect project or investment data that can be easily disaggregated at the urban scale and/or capture urban NbS characteristics and benefits. Data on nonmonetized urban co-benefits are aggregated in other data sets like neighborhood health statistics or even insurance maps. Exceptions include earmarked funding that specifically target and track non-economic goals like GHG emission mitigation or green investment funds. All these factors lead to significantly limited international estimates.
Analysis of the available data sources reveals the conventional NbS receives most of the funds, while urban-focused NbS funding is more limited despite the fact that cities produce 70-80 percent of global GDP.
38 An example is urban tree-planting. Often rolled into local transportation or parks and recreation budgets, these programs are rarely funded at scale by development banks and other investment entities.
39 This figure is based on the Green Climate Fund assessment that 70 percent of known climate solutions are within the boundaries of subnational authorities and the SFN 2021 estimate of the needed expenditure in nature: $536 billion per year.
3. Case Studies of Successful NbS
Six case studies highlight the multiple benefits of urban NbS in cities and demonstrate that in order to mainstream urban NbS cities need new business models and policies and governance capacity support. A growing number of mayors are embracing nature-based solutions as part of their climate agenda, often associating it with such other issues as equitable development or environmental justice. They design and adopt municipal climate action plans incorporating nature-based projects and have found innovative ways to fund these initiatives, frequently with support from international city networks or multilateral development banks. Given the type of goods and services provided at the urban level, most projects with a nature-based approach are nested as components in larger projects dealing with resilience, mobility, stormwater management and so forth. The first three case studies involve urban greening investments. The last three case studies look at water management strategies, including coastal marine environments.
Urban Greening Case Studies
Urban greening projects may include enhancing street systems through green corridor projects with tree planting programs; water absorbing green spaces; integrated green and gray infrastructure for stormwater management and additional recreational spaces; and expansion of parks and open space networks. The three examples highlight different realities cities from the Global North and South encounter when implementing NbS across a range of conditions in cities at different stages of executing their greening policies. One is in a medium sized city in a more populous metropolitan area, the others are the dominant cities in less populous metropolitan areas. While all are experiencing steady population growth, each has differing rates of urban development, states of infrastructure, municipal technical capacities, and levels of employment and poverty rates. The level of natural resources varies, with a large stock of privately owned trees in one city, while another is highly deforested. Their planning and financing are also different, one being self-financed, one reliant on grants from external sources and the third, a hybrid of local and external funding.
1.Melbourne, Australia - Urban Forestry
Exposure to climate extremes from heavy rains to bush fires to drought – especially the Millennium drought (1997- 2009) – made Melbourne’s leadership, with strong electoral support, realize the need to incorporate nature throughout their city (population 170,000). The city embarked on developing a holistic greening approach in 2011. Following the issuance of its updated comprehensive plan, Future of Melbourne 2026 in 2016 that made caring for the environment its first goal, the city issued three implementing strategies, including its Urban Forest Strategy (UFS, 2017). See Figure 4, below.
The UFS aims to increase the city’s public tree canopy from 22 percent to 40 percent by 2024 to relieve urban heat island effects, create healthier ecosystems, and increase biodiversity. The city supports the UFS with a dedicated budget line projected to be about half a million dollars/year (approximately 0.1 percent of the total budget through 2026).40 Under the strategy, any proposed removal or pruning of a public tree requires written permission of the City of Melbourne Arborist that includes the disclosure of the tree’s value (based on amenity and ecosystem service calculations according to the tree’s dimensions – height, caliper, species and canopy), removal costs, and the price of reinstatement of the growing environment for the replacement. The result is a payment into the city’s Urban Forest Fund (founded 2017) that covers the replacement and uses excess funds to provide matching grants for new greening projects on private or public property lacking trees/vegetation.41 To date, the city has planted 70,000 trees under this program.
40 City of Melbourne, 2022.
41 Thomas, Interview, 2022.
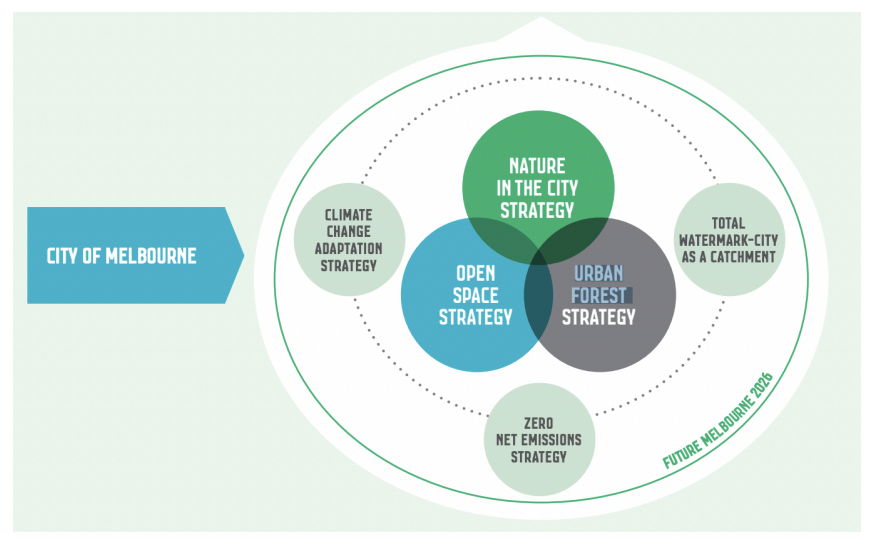
Figure 4. City of Melbourne Green Strategy. Melbourne’s holistic greening approach is aligned with the city’s comprehensive plan, encompasses mitigation and adaptation and is associated with specific NbS strategies. Source: City of Melbourne
2. Freetown, Sierra Leone – Landslide Risk Reduction
As with Melbourne, an urban disaster in 2017, namely a landslide killing more than 1,000, displacing 5,000 with property damages in the millions, led Freetown (population 1.2 million) under the mayoral leadership of Yvonne Aki Sawyerr to engage its citizens in an extensive planning process to address the dual issues of sustainable development and climate change, that yielded its Transform Freetown plan. 42 Resilience is among its four major priorities. It incorporates a cluster of activities that includes tackling the dramatic deforestation that accompanied the city’s rapid urbanization in the past two decades.
Aiming to reduce the risks associated with extreme heat, landslides, and flooding, the city is implementing its 1 million tree planting plan and an associated grassroots economic development campaign, #FreetowntheTreetown. Starting in 2020, the city partnered with two NGOs, the Environmental Foundation for Africa and Greenstand, to plan the planting and develop an employment program for monitoring and caring for the trees. It secured a share of a $57 million GEF grant, “Resilient Urban Sierra Leone Project,” awarded to the national government in 2021 to support key development issues: municipal capacity-building and infrastructure investment. The program also won a million-dollar grant and capacity support from Bloomberg philanthropies.43
The #FreetowntheTreetown campaign has been working to overcome difficulties in its short existence, from an adverse political landscape to local disasters (e.g., a fuel tank explosion in November 2021 and a massive fire in an informal settlement in March 2022). Nonetheless, to date, the city has planted 560,000 trees, restored 578 hectares, and generated more than 1,200 jobs, mainly for youth and women. The city equipped the new “tree growers” with a specially designed digital app to geo-tag and document tree growth in exchange for micropayments. Innovatively, the city recently labeled its 5,000 geo-tagged trees as “tree-impact tokens,” available for sale to organizations and businesses in an effort to create a tree trading market to finance additional planting.44 The program has gained international attention for these innovations and other cities have expressed an interest in replicating the program.
42 Yvonne Aki-Sawyerr, 2019.
43 IRBD, 2021.
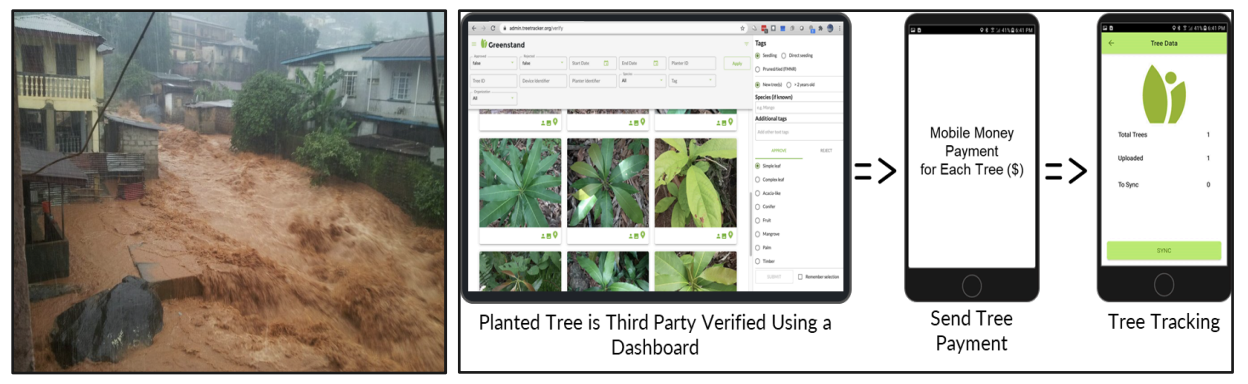
Figure 5. Freetown - From landslides to Reforestation. After experiencing huge human and material losses from a landslide (right), Freetown began a tree planning program and an associated technology-based maintenance initiative (left) whose cobenefits include increased resilience and economic development Source: #FreetowntheTreetown app. Source: World Bank.
3. Monterrey, Mexico - Green Deal Policy
Monterrey, Mexico (population 1.1 million) offers an example of governance reform and stakeholder engagement. The city has been engaging with the private sector to invest in the Green Deal (Acuerdo Verde) climate program, developed under the city’s Mayor Riojas (elected in September, 2021). In early summer 2022, after appointing a Sustainable Cities Cabinet (composed of departments of infrastructure, public services, human development and sustainable urban development), the mayor joined the business and academic communities to create a sevenmember Joint Commission on Urban Development, Mobility and Sustainable Infrastructure to advance an ongoing dialogue with the city’s developers.45 The aim is to smooth the way for their investment in green infrastructure in exchange for fast-track permits. Developers can either donate land for the city to build a public project (from the city’s Green Deal project pipeline) or support the construction of a park or green space jointly with the city on public land. The Commission monitors the project according to Monterrey’s NbS criteria, supervises the building process, and enforces quality guidelines.46
Water Management Case Studies
The three case studies below demonstrate that many investments in urban NbS occur at a regional scale beyond municipal boundaries with a significant positive impact on the urban core. As cities in the Global south grow quickly, often informally, maintaining access to healthy and sustainable potable water sources and reducing the risk of waterrelated disasters is critical. Conversely, as climate change accelerates, urban water use impacts the planet’s health in areas like biodiversity, habitat loss, and hydrological cycles. Nature-based solutions that support urban water management can include coastal and riverine disaster risk reduction efforts and ecosystem conservation and restoration. Funding here comes from many sources, but primarily the public and philanthropic sectors.
4. Singapore - Coastal Marine Management
Singapore (population 6 million), an island city-state that depends heavily on its coastal and marine environment for shipping, industrial production and residential development is implementing an integrated urban coastal management (IUCM) system initiated in 2007. Its extensive regulatory framework encompasses ten plans including its master plan, climate action plan, and several sectoral plans (e.g., Singapore Blue Plan, Parks and Waterbodies Plan). It boasts 35 regulations covering resource management, biodiversity, pollution control and waste management, marine activities, coastal hazard management and heritage conservation and is managed by an interministerial coordinating committee that oversees a Technical Committee on Coastal and Marine Environment and the Biodiversity and Environment Database System (BIOME), which also provides a repository of Singapore’s flora and fauna, plants and animals and other environment related data.
45 Gobierno de Monterrey, June 6, 2022.
46 Ballesteros, Interview 2022.
The Sungei Buloh Nature Park Network initiative is an associated project that incorporates massive mangrove restoration – between 1958-2014 Singapore lost 80 percent of its mangroves to land reclamation, freshwater reservoir, and aquaculture projects. The initiative will restore 400 hectares of mangroves, 15 kilometers of walking trails in areas formerly restricted, and a build an educational center for use in building citizen awareness of the benefits of mangroves for biodiversity.47
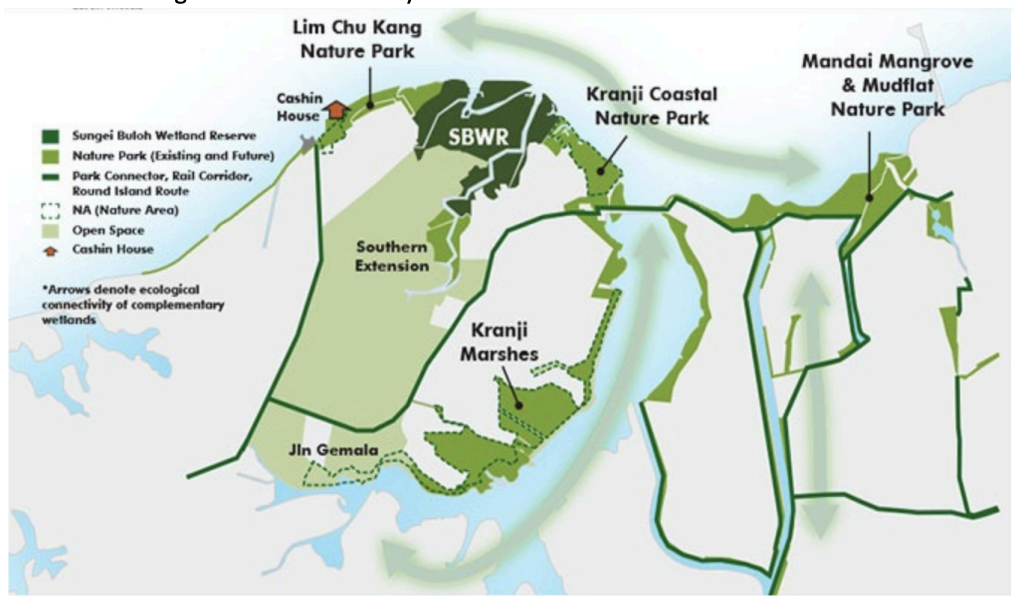
Figure 6. Singapore Sungei Buloh National Park Network. Source: National Parks Board
5. Quelimane, Mozambique - Coastal Mangrove Restoration
Quelimane, Mozambique (population 467,000), faces severe weather conditions and lacks adequate infrastructure to safeguard the population from the effects of climate change. Located at the head of the Bons Sinais estuary, one of the largest concentrations of mangroves along the east coast of Africa, the city has experienced rapid population growth – a 200 percent increase – in the past 25 years. Dramatic changes in land use have accompanied this growth: developed land increased 79 percent; mangroves and wetlands decreased 28 percent.48 Several sources fueled (and continue to fuel) the depletion: the use of mangrove wood for cooking and housing materials and the clearing of mangroves and wetlands for agriculture (rice), aquaculture (shrimp), and salt pans. See Figure 3.
Nevertheless, in 2015, the city and another nearby city, Pemba, began implementing a restoration project with $15 million in technical and financial support from USAID.49 An important component of the project has been to work closely with the community, raising awareness of the importance of the mangroves and encouraging an active involvement from Quelimane residents, particularly women in managing and conserving the new planting in mangroves restored in the city’s poorest areas. Support from World Vision and UN Habitat has been a key aspect of the project. They have been developing alternatives for housing materials and cooking fuel.
Finally, the project included the creation of vulnerability maps employed in land use planning and permitting.50 However, in the Global South, mayors must deal with such pressing issues as extreme poverty, disease, provision of basic infrastructure and other development issues often acting without knowledge of the importance or technical know-how to include NbS in their efforts. This situation emphasizes the need for capacity building within local government and among funders and for the integration of financing climate action with development funding.51
47 Jabson Berhane Alemu I, 2020.
48 Noca Furaca, et.al., 2021.
49 US AID, 2015.
50 Lee Gerston, et.al., 2018.
51 Araujo, Interview 2022.

Figure 7. The Growth of Quelimane Mozambique and the Fate of Mangroves and Wetlands (Cleared mangroves and wetlands make room for development (right); house constructed with mangrove materials (Source: Unaite, 2017)
6. Quito, Ecuador - Water Fund
Cities have found interesting opportunities to fund NbS through international cooperation coming from NGOs and other partners. The first water fund launched by The Nature Conservancy (TNC) was established in Quito, Ecuador (population 2.8 million) in 2000. After seven years the Municipal Council approved the ordinance which stated that 2 percent of the water utility company revenues had to go to the Fund. The Quito Water Fund (FONAG) was established as an 80-year trust fund that receives revenues from water users, public utilities, private companies and NGOs to fund NbS. FONAG doubled its return on investment, improving watershed function, water supply and water quality. FONAG’s successful model has been replicated throughout Latin America and has generated interest throughout the world. In 2011 the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), the FEMSA Foundation, the Global Environment Facility (GEF), International Climate Initiative (IKI) and TNC created the Latin American Water Funds Partnership for contributing to water security in Latin America and the Caribbean through the creation and strengthening of water funds.
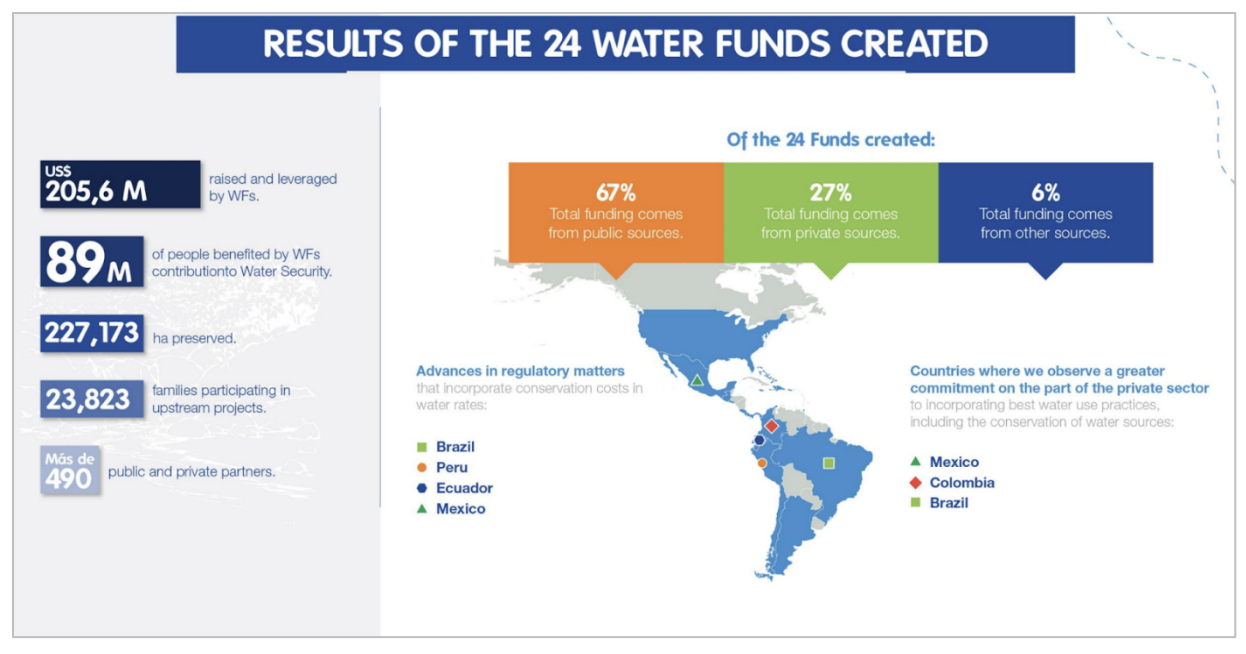
Figure 8. Results of 24 Water Funds, including Quito Ecuador
4. Call-to-Action: Increasing NbS Investments in Cities
Successful urban NbS show that while they are viable to implement, much more effort is needed to mainstream urban NbS investments and demonstrate their value to urban stakeholders. As the impacts of climate change become more evident – recent heat waves with record-breaking temperatures in different regions of the world being an example – awareness is growing that investments in nature are resilience-building measures. The growing scale of these stresses puts pressure on local authorities to find effective ways to work with nature when investing in city services.
Five lines of actions have emerged from this assessment that would enhance investments in urban NbS to address climate change:
1. Accelerate Investments in urban NbS. Funders can:
- Support mainstreaming efforts that connect urban NbS with adaptation and mitigation strategies that reduce the damaging effects of climate change in urban places with more public decision-makers, funders and philanthropes. 52
- Advocate for a greater priority on urban NbS strategies in urban development funding. Urban NbS funding is clearly in the incipient stage. Based on the 2022 SFN report the estimated the global NbS financing gap, and the Green Climate Fund assertion that “Seventy percent of known climate solutions are located within the boundaries of subnational authorities”, the need for subnational NbS would be about $450 to 700 billion annually, with urban NbS being some fraction of this sum.
2. Expand NbS awareness campaigns to expand and present compelling evidence on how urban NbS provides greater urban resilience. Urban NbS practitioners and supporters can:
- Engage mayors and city officials already supporting urban NbS as city champions to help inform and educate national and subnational, public, and private sector decision-makers about the importance of investing in nature.
- Demonstrate the value of investing in urban NbS for addressing mitigation with long-term climate change adaptation.
- Demonstrate the benefits of urban NbS investments, including risk and cost reduction from increasingly damaging natural disasters.
- Support stronger alignment of national and subnational NbS strategies with urban-focused NbS.
3. Provide governance and technical support to municipal agencies to restructure local governance that supports NbS. Local policymakers and practitioners can:
- Consider how to restructure local governance to coordinate municipal agencies’ investment in NbS and support greater alignment of subnational and national approaches to urban NbS, including climate action planning.
- Work with public and private sector entities to develop viable projects incorporating NbS from inception to implementation that can serve as pilot programs, and upscale successful programs.
- Ask for training and capacity support for subnational governments as well as for private sector partners and investors.
4. Develop research to determine how to track global urban NbS investments that enables public and private decision-makers to develop a more holistic portfolio of urban NbS investments. Researchers can:
- Expand on this paper’s preliminary approach for identifying metrics, data, funding flows and valuation methods, which could underlie an improved estimate of the gap between current and needed funding.
- Engage stakeholders broadly in how urban NbS can integrate with existing CAPs and land use planning programs.
- Fund additional technical assistance to align subnational and national approaches to urban-focused financing in nature, as well as to develop, implement, and monitor urban NbS
5. Build a global database to assess and monitor urban NbS conditions, programs, and funding. Researchers and practitioners should work together to:
- Identify data criteria and database framework that can be useful for both funders and cities to tracking urban NbS more holistically.
- Work with data managers to develop a strategic plan for the ownership, maintenance, and monitoring of urban NbS data that can help funders and cities incorporates its unique features holistically across planning efforts including climate action plans (CAPs), integrated land use planning, and government budget priorities.
Long-term biodiversity and ecosystem health depends on strong, synergistic NbS relationships along an urban-rural continuum. Reconnecting cities back to nature and integrating NbS in urban land use and infrastructure decision-making and investment strategies is a critical element of an effective climate change portfolio and successful urban NbS show that it is possible to implement. However, urban NbS categories are absent from comprehensive global NbS funding. This gap presents a challenge for funders. Nonetheless, preliminary data exists and offers an indication that, like NbS generally, NbS in cities are severely underfunded. A new conceptual paradigm that values, identifies, tracks, and evaluates urban NbS would enable public and private decision-makers to develop holistic portfolios to address the environmental and socioeconomics impacts of climate change more effectively. This research provides a clear call to action for public, private, and philanthropic stakeholders to work together to reconnect cities to nature for the health and well-being of ecosystems and urban communities.
Abell, R., and et al., Beyond the Source: The Environmental, Economic and Community Benefits of Source Water Protection. The Nature Conservancy, 2017.
Altamirano, M. A., and et al., Handbook for the Implementation of Nature-Based Solutions for Water Security: Guidelines for Designing an Implementation and Financing Arrangement. 1st Edition, EU Horizon 2020, http://naiad2020.eu/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/D7.3REV.pdf.
Ballasteros, Laura. Secretary of Sustainable Urban Development, City of Monterrey. Zoom, 28 July 2022.
Barnwal, Aloke. “NBS in SCIP Projects.” Aug. 2022. ---. Senior Climate Change Specialist, GEF. Zoom, 29 July 2022
Caro, Esperanza. Director General of Sustainable Development, City of Seville. Zoom, 10 Aug. 2022.
Carsten, Nessover, and et al., “The Science, Policy, and Practice of Nature-Based Solutions: An Interdisciplinary Perspective.” Science of Total Environment, vol. 579, 2016, pp. 1215–27, https://www.academia.edu/33319883/The_science_policy_and_practice_of_na… erdisciplinary_perspective.
Chng, Li Chang, et al. “Environmental Performance Indicators for the Urban Coastal Environment of Singapore.” Regional Studies in Marine Science, vol. 49, Jan. 2022, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2021.102101.
City of Melbourne. Budget 2022-2023. ND, p. 187, https://www.melbourne.vic.gov.au/SiteCollectionDocuments/budget-2022-23…. ---. Nature in the City Thriving Biodiversity and Healthy Ecosystems Summary. 2018, p. 5, https://www.melbourne.vic.gov.au/sitecollectiondocuments/nature-in-the-…. ---. Tree Policy 2021. p. 2021, https://www.melbourne.vic.gov.au/SiteCollectionDocuments/tree-policy-2021.pdf.
Climate Policy Initiative. Global Landscape of Climate Finance. Climate Policy Initiative (CPI), Dec. 2021,https://www.climatepolicyinitiative.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/Full….
Cohen-Shacham, E., et al. Nature-Based Solutions to Address Global Societal Challenges. IUCN, 2016, https://serval.unil.ch/resource/serval:BIB_93FD38C8836B.P001/REF.
de Araujo, Manuel. Mayor, City of Quelimane. Personal Communication, 15 Aug. 2022. Faivre, Nicholas, and el al., “Nature-Based Solutions in the EU: Innovating with Nature to Address Social, Economic, and Environmental Challenges.” Environmental Research, vol. 159, no. November 2017, pp. 509–18, https://www-sciencedirect-com.proxy.library.upenn.edu/science/article/pii/S0013935117316080.
Furaca, Noca, et al. “Exploring Urbanization and Critical Habitat Lossthrough Land Cover Change around the Bons Sinais Estuary, Mozambique.” WIO Journal of Marine Science, vol. Special Issue 1, 2021, pp. 43–58, https://www.academia.edu/78937466/Exploring_urbanization_and_critical_h… _change_around_the_Bons_Sinais_Estuary_Mozambique.
Gerston, Lee, et al. Mozambique Cities Adapt to Climate Change One Tree and One Text Message at a Time. Chemonics, 2018, p. 2, https://www.chemonics.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/2015-Frontlines-ClimateIssue-CCAP.pdf.
Gilbert, Jane. Chief Heat Officer, Miami Dade County. Zoom, 15 Aug. 2022.
Global Platform for Sustainable Cities, World Bank. Biodiversity and Natural Asset Valuation in Cities. World Bank, 2019, https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/287521568801462241/pdf/TechnicalPaper.pdf.
Gobierno de Monterrey. Firma Gobierno de Monterrey Acuerdo con desarrolladores por Infraestructura Verde y Recuperación Económica. https://www.monterrey.gob.mx/busqueda/Noticia/firma-gobierno-de-monterreyacuerdo-con-desarrolladores-por-infraestructura-verde-y-recuperacion-economica.
Goeransson, Susan, and Sarah Duff. Director of Infrastructure Group and Principal of Green Economy and Climate Action. ERBD. Personal Communication, 10 Aug. 2022.
Green Climate Fund. “The Global Subnational Climate Fund (SnCF Global), Catalyzing Climate Solutions at the Local Level.” Green Climate Fund, 2022, p. 2, https://www.greenclimate.fund/sites/default/files/document/sncfcase-study.pdf.
Greg Browder, et al. Integrating Green and Gray, Creating the Next Generation of Infrastructure. World Bank and World Resources Institute, 2019, https://www.naturebasedsolutions.org/sites/default/files/2021- 02/GreenGreyInfrastructureFlagship.pdf
Guerry, Anne D., and et al., Urban Nature and Biodiversity for Cities. Global Platform for Sustainable Cities World Bank, Sept. 2021.
Hand, Dean, et al. 2020 Annual Impact Investor Survey. Global Impact Investing Network, 11 June 2020, https://thegiin.org/research/publication/impinv-survey-2020.
Holzinger, Oliver, and Nick Grayson. Birmingham Health Economic Assessment & Natural Capital Accounts, Revealing the True Value of Council-Managed Parks and Green Estate. Birmingham City Council and Consultancy for Environmental Economics & Policy, July 2019, p. 67.
ICLEI. Nature Based Solutions for Sustainable Urban Development. 2017, https://unfccc.int/files/parties_o
InterAmerican Development Bank. PROGRAMA INTEGRAL DE DRENAJE PLUVIAL EN CIUDADES PRIORIZADAS DEL PERÚ (PE-L1238). 2019, p. 36, https://idbdocs.iadb.org/wsdocs/getdocument.aspx?docnum=EZSHARE11824115…;
Jongman, Brenden. Senior Disaster Risk Management Specialist, World Bank. Personal Communication, 19 July 2022.
L., Chan, et al. Handbook on the Singapore Index on Cities’ Biodiversity. Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity and National Parks Board, 2021, https://www.nparks.gov.sg/-/media/nparks-realcontent/biodiversity/singapore-index/handbook-on-the-singapore-index-on-cities-biodiversity-cbd-ts98.ashx.
Mackinnon, Brendan, and Ramkumar Narayanan. Private Impact Fund Report 2021. Nov. 2021, p. 130, https://tameo.solutions/research.
Marsters, Lizzie, Ana Gabriela Morales, et al. Nature-Based Solutions in Latin America and the Caribbean: Financing Mechanisms for Regional Replication. Inter-American Development Bank and World Resources Institute, 2021, https://files.wri.org/d8/s3fs-public/2021-10/nature-based-solutions-in-latin-america-and-the-caribbeanfinancing-mechanisms-for-replication_0.pdf?VersionId=vB60gcYroVaMVXNYKHt9dxMA4VPzosgw.
Matsumoto, Tadashi. Head of Sustainable Urban Development Unit, OECD. Personal Communication, 11 Aug. 2022.
Matthews, John, and Ernesto Ocampo Dela Cruz. Integrating Nature-Based Solutions for Climate Change Adaptation and Disaster Risk Reduction: A Practitioner’s Guide. Asian Development Bank, 2022, https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/801226/nature-based-solutions-cca-drm.pdf.
McDonald, Robert, and Daniel Shemie. Urban Water Blueprint, Mapping Conservation Solutions to the Global Water Challenge. The Nature Conservancy and C40, 2014, https://water.nature.org/waterblueprint/#/section=overview&c=3:6.31530:-37.17773.
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine. Review of the New York City Watershed Protection Program, 2020, https://nap.nationalacademies.org/download/25851.
National Trust and Heritage Lottery Fund. Natural Capital Accounts for Public Green Space in London. Greater London Authority, 2017, p. 35, https://ecosystemsknowledge.net/sites/default/files/wpcontent/uploads/Fullpercent20reportpercent20naturalpercent20capitalpercent20accountspercent.
NCAVES and MAIA. Monetary Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Ecosystem Assets for Ecosystem Accounting: Interim Version, 1st Edition. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Statistics Division, 2022.
OECD. Biodiversity: Finance and the Economic and Business Cycle for Action, A Report Prepared by the OECD for the French G7 Presidency and the G7 Environment Ministers’ Meeting 5-6 May 2019. OECD, 2019. ---. Nature-Based Solutions for Adapting to Water-Related Climate Risks. 2020, https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/docserver/2257873den.pdf?expires=1658704153&id=id&accname=guest&checksum=55A8424838ABB65D9AB6E213061FE555
Oliver, Emmie, et al. Nature-Based Solutions in Latin America and the Caribbean: Support from the Inter-American Development Bank. Inter-American Development Bank and World Resources Institute, 2021, https://files.wri.org/d8/s3fs-public/2021-10/nature-based-solutions-in-latin-america-and-the-caribbean-support-from-the-inter-american-developmentbank_0.pdf?VersionId=Ts3XB_gso0yCgcGKWNY5UbHZcv_blC8r.
Orloff, Mariana, et al. Senior Manager for Urban Development, Acting Global Director of the Center for Sustainable Cities, and Implementation Manager of Cities4Forests. WRI. PersonalCommunication, 15 Aug. 2022.
Ozment, Suzanne, et al. Nature-Based Solutions in Latin America and the Caribbean, Regional Status and Priorities for Growth. 2021, https://www.wri.org/research/nature-based-solutions-latin-america-and-caribbeanregional-status-and-priorities-growth.
Pearce, Reagan. “What Are Ecosystem Services?” Earth Org, 6 Oct. 2020, https://earth.org/what-are-ecosystemservices/.
Pegasus Capital Advisors. “FP152: Global Sub National Climate Fund (SnCF Global) – Equity.” Green Climate Fund, 9 Dec. 2020, https://www.greenclimate.fund/sites/default/files/document/funding-proposal-fp152.pdf.
PEMSEA. PEMSEA Annual Report 2021: From Recalibration to Action. Partnerships in Environmental Management for the Seas of East Asia. 2022, p. 113, http://pemsea.org/sites/default/files/PEMSEApercent20Annualpercent20Rep…(FIN AL)percent2020220628.pdf.
Pinko, N., et al. Financial Aggregation for Cities. Cities Climate Finance Leadership Alliance, June 2022, https://www.climatepolicyinitiative.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Financial-Aggregation-for-Cities.pdf
Steven, A. D. L., et al. Coastal Development: Resilience, Restoration, and Infrastructure Requirements. World Resources Institute, 2020, https://oceanpanel.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/Coastal-Development-FullPaper-Final.pdf.
Swann, Stacy, et al. Public International Funding of Nature-Based Solutions for Adaptation: A Landscape Assessment. World Resources Institute, 2021, https://files.wri.org/d8/s3fs-public/public-internationalfunding-nature-based-solutions-adaptation_0.pdf.
Technical Committee on the Coastal and Marine Environment. Singapore’s Integrated Urban Coastal Management. National Parks Board, 2018, p. 22, https://www.nparks.gov.sg/-/media/nparks-realcontent/biodiversity/programmes-and-initiatives/nparks_iucmbooklet_nov2018.ashx?la=en&hash=971CB0816BE4829D7C8B62775588BFA00F25C2B6
The Global Commission on the Economy and Climate. Unlocking the Inclusive Growth Story of the 21st Century, Accelerating Climate Action in Urgent Times. New Climate Economy, 2018, https://newclimateeconomy.report/2018/wpcontent/uploads/sites/6/2019/04/NCE_2018Report_Full_FINAL.pdf
Thela, Carolina, and Patricia Himschoot. Municipal Staff, City of Buenos Aires. Personal Communication, 4 Aug. 2022.
Thomas, Freya. Senior Urban Forester, City of Melbourne. Personal Communication, 10 Aug. 2022.
Uniate, Mustafa Cesar Paulino. Analysis of Causes and Possible Methods of Dealing with Mangrove Deforestation in Mozambican Coastal Areas: A Case Study of Quelimane District in Zambézia Province. World Maritime University, 2017, https://commons.wmu.se/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1575&context=all_dissertations.
United Nations Environment Assembly of the United Nations Environment Program. Resolution Adopted by the United Nations Environment Assembly on March 2, 2022 Nature Based Solutions for Supporting Sustainable Development. UNEP/EA/Res.5, https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/39864/NATUREBASED… MENT.percent20English.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y.
United Nations Environment Programme. State of Finance for Nature, Tripling Investments in Nature-Based Solutions by 2030. 2021, https://www.unep.org/resources/state-finance-nature.
United Nations Office of Disaster Risk Reduction. Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2022, Our World at Risk: Transforming Governance for a Resilient Future. 2022, https://www.undrr.org/gar2022-ourworld-risk#container-challenge.
University of Liverpool. Accounting for Natural Capital in Cities: Making the Invisible Visible. May 2022,https://www.liverpool.ac.uk/media/livacuk/publicpolicyamppractice/jo/Ac… n,Cities,FINAL.pdf.
US AID. Coastal City Adaptation Project (CCAP) Agreement No. AID-656-C-14-00001. 2015, https://pdf.usaid.gov/pdf_docs/PA00KTK1.pdf.
Wild, Tom, et al. Nature-Based Solutions: State of the Art in EU-Funded Projects. European Commission, 2020
World Bank. A Catalog of Nature Based Solutions for Urban Resilience. 2021, https://www.naturebasedsolutions.org/knowledge-hub/50-catalogue-nature-based-solutions-urban-resilience.
---. Consolidated Climate Finance Gap Fund Annual Report 2021. World Bank, 2022, https://www.citygapfund.org/sites/default/files/2022-05/220514-gap-fund…;
---. Natural Asset and Biodiversity Valuation in Cities. June 2019, https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/287521568801462241/pdf/Tech…;
---. Nature-Based Solutions for Disaster Risk Management. World Bank, 2018, https://naturebasedsolutions.org/sites/default/files/2021- 02/NBSpercent20forpercent20DRMpercent20booklet.pdf.
---. Overview, Urban Development. https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/urbandevelopment/overview.
---. “Understanding Poverty Community-Driven Development.” Decentralization, 6 June 2013. World Bank, World Resources Institute and PROFOR. Nature-Based Solutions for Disaster Risk Management. World Bank, 5 May 2022, https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/253401551126252092/pdf/Book….


