Key Message
Nature-based solutions can help cities become more resilient, healthy and equitable. But for urban nature to reach its full potential, investments need to be substantially scaled up. In 2020, NbS received just 0.3% of overall spending on urban infrastructure, and investments are unequally distributed across and within cities. With this publication, UNEP and the Penn Institute for Urban Research outline gaps and opportunities for NbS financing in cities, best practices from around the world, and actions that local governments, financial stakeholders, private sector and knowledge partners can take to scale up investments for nature in cities.
Introduction
The State of Finance for Nature (SFN) annual report series tracks finance flows to naturebased solutions (NbS) and compares them to the investment needed to maximise the potential of NbS to help tackle climate, biodiversity and degradation challenges. For the first time, this edition estimates the scale of nature-negative finance flows from both public and private sector sources globally. The figure is daunting – almost US$7 trillion per year - and is likely to be an underestimate given it includes only direct impacts. Private finance flows that have a direct negative impact on nature are US$5 trillion, which is 140 times larger than private investments into nature-based solutions (NbS).
On the public side, environmentally harmful subsidies have increased by 55 per cent to US$1.7 trillion since the last report, despite government commitments, and driven by fiscal support for fossil fuel consumption. The combined impact of public and private nature-negative finance flows is enormously destructive and undermines potential increases in finance for NbS. However, this misalignment represents a massive opportunity to turnaround private and public finance flows to align them with Rio Convention targets.
Meanwhile, NbS remain severely underfunded. Current finance flows to NbS are US$200 billion, only a third of levels needed to reach climate, biodiversity and land degradation targets by 2030. Governments continue to provide most funding for NbS (82 per cent). Despite the irrefutable need for action and growing commitments, e.g. zero-deforestation pledges in the agri-food sector, NbS finance has increased only 11 per cent since the 2022 edition.
NbS provide critical investment opportunities as they are cost-effective and provide multiple benefits. Investment opportunities in sustainable land management can increase fourfold by 2050 based on long-term profitability of sustainable food and commodity production - critical to catalyse private investment. Protection of diverse ecosystems is highly cost-effective and represents 80 per cent of additional land area needed for NbS while absorbing only 20 per cent of additional NbS finance by 2030. Given the scale of degradation globally, restoration provides massive opportunities to strengthen ecosystem function and resilience to deliver the ecosystem services that people rely so heavily upon.
However, despite the sizeable investment potential of NbS, the single most impactful action to reduce and halt nature loss is the realignment of nature negative finance flows. Due to their massive scale, realignment of public and private nature-negative finance flows will have a very significant impact and is essential to avoid undermining investment in NbS. While more public finance for NbS is critical, more action is needed to repurpose harmful subsidies. In parallel, governments need to put in place regulation and economic incentives to turn private finance flows away from nature harming activities and toward nature and nature-based solutions. Meanwhile, the financial sector and the business community at large cannot wait for a fully developed enabling policy environment. There is much they can and must do now to urgently transform unsustainable business models.
In short, a major turnaround for nature is needed. Unless the real economy and financial system reduce financing of nature-negative activities (i.e. greening finance), actions to scale up investment in NbS (i.e. financing green) will be insufficient to tackle the climate, biodiversity and degradation crises.
This document provides a summary of the key findings and recommendations of the full SFN 2023 report.
Key findings
Nature-negative finance flows
Annual finance flows from public and private sources that have direct negative impact on nature are estimated at almost US$7 trillion per year.
Private nature-negative finance
For the first time, global private finance flows that have a direct negative impact on nature have been estimated, and they are very large indeed at US$5 trillion per year (around 5 per cent of global GDP).
- For the first time, global private finance flows that have a direct negative impact on nature have been estimated, and they are very large indeed at US$5 trillion per year (around 5 per cent of global GDP).
- This is likely to be an underestimate as nature-negative finance with indirect impacts is not included.
- The five industries channelling most of the negative financial flows – construction, electric utilities, real estate, oil and gas, and food and tobacco – represent 16 per cent of total private investment flows in the economy but 43 per cent of nature-negative flows.
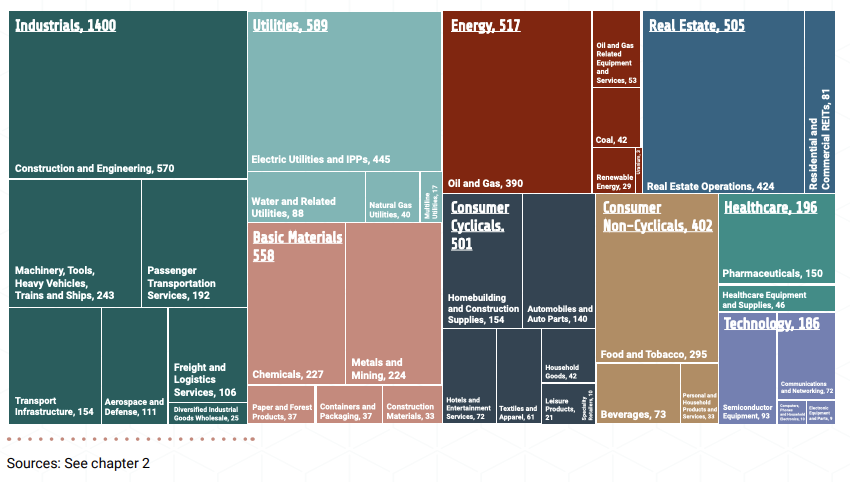
Figure 1. Nature-negative private finance by sector, $ billion (2023 US$)
Public nature-negative finance
Tracked nature-negative public finance flows, estimated at almost US$1.7 trillion in 2022 (Figure 2), are more than 10 times greater than public finance flows to NbS (US$165 billion).
- Almost 90 per cent of tracked negative public flows (EHS) are directed to fossil fuels (69 per cent) and agriculture (20 per cent).
- Fossil fuel subsidies to consumers doubled from US$563 billion in 2021 to US$1,163 billion in 2022.
- In addition to the US$600 billion increase in fossil fuel consumption subsidies, IEA estimates extra spending of US$500 billion to lower energy costs in 2022, with US$350 billion in Europe following the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
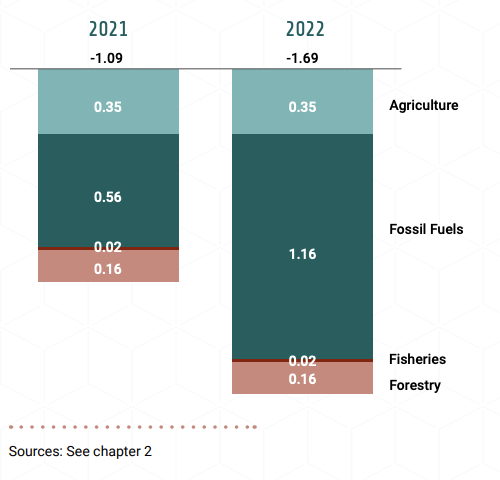
Figure 2. Environmentally harmful subsidies, $ trillion (2023 US$)
Current finance flows to Nature-based Solutions
SFN 2023 estimates that total annual finance flows to NbS in 2022 were roughly US$200 billion (Figure 3) – only one-third of NbS finance needed by 2030.
- NbS finance has increased by 11 per cent since SFN 2022.
- Governments continue to lead, providing 82 per cent (US$165 billion) of total NbS finance flows. Nevertheless, public finance flows to NbS were less than one-tenth of public spending on environmentally-harmful subsidies in 2022.
- Private finance for NbS remains modest at US$35 billion (18 per cent of total NbS finance flows). Over half is channelled through biodiversity offsets and sustainable supply chains.
- Private finance flows to NbS are less than 1 per cent of private finance flows that have a direct harmful impact on nature.

Figure 3. Public and private finance flows to NbS in 2022, $ billion (2023 US$)
Future investment needs and opportunities
Finance flows to NbS need to almost triple from current levels (US$200 billion) to reach US$542 billion per year by 2030 and to quadruple to US$737 billion by 2050 to meet Rio Convention targets (Figure 4).
- Annual NbS investment opportunities in sustainable land management (SLM) will likely increase fourfold from US$63 billion in 2025 to US$241 billion by 2050.
- As many SLM NbS generate financial revenues, SLM provides an important opportunity for private investment and is critical to scale NbS finance.
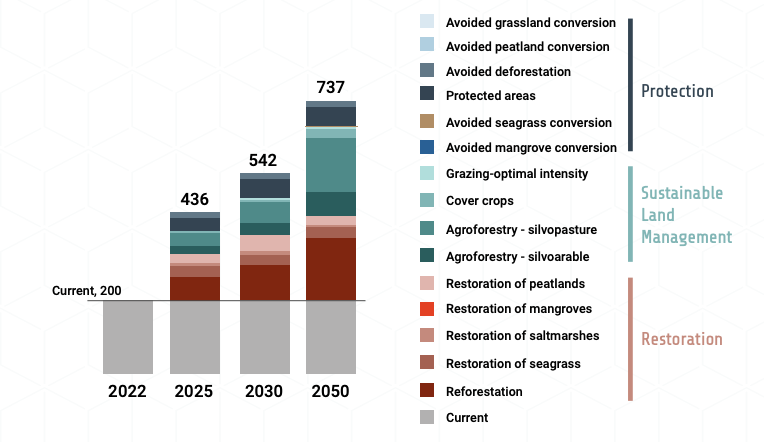
Figure 4. Additional annual finance need, Rio-aligned, $ billion (2023 US$)
- Restoration NbS potentially requires the highest levels of investment at over US$177 billion per year by 2030, which is over half of annual NbS finance due to its relatively high cost and the global extent of degradation.
- Protection-related NbS represent roughly 80 per cent of additional land area needed for NbS (Figure 5) by 2030 while absorbing only 20 per cent of additional NbS finance. This reflects the increase in area of protection needed to reach the 30x30 target and the relative cost effectiveness of protection.
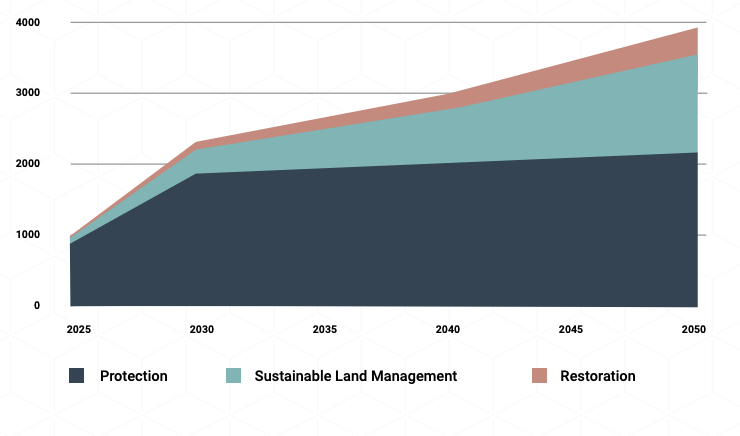
Figure 5. Additional cumulative land area by NbS 2025-2050, Rio-aligned, Mha
Both public and private finance flows to NbS will need to dramatically increase to close the finance gap between current finance flows and the investment needed to meet Rio targets.
- While both public and private NbS finance flows will steadily increase to 2050, private finance can potentially increase its share of NbS finance from 18 per cent currently to 33 per cent by 2050.
- Total annual NbS finance from private sources can reach over US$100 billion by 2030, almost three times current levels.
- • Public investment will continue to play a critical role. Government annual expenditure on NbS needs to quickly increase from current levels (US$165 billion) to US$359 billion (an increase of US$194 billion) by 2025 and to US$439 billion (an increase of US$274 billion) by 2030.
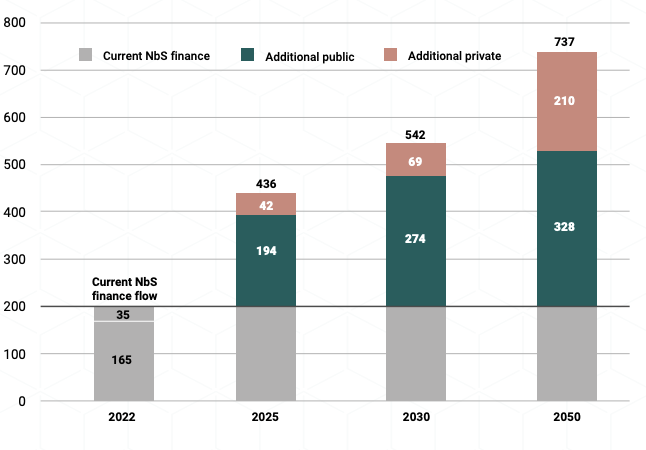
Figure 6. Additional NbS finance needed from public and private sources, Rio-aligned, $ billion (2023 US$)
Synthesis
Governments are very unlikely to meet their international climate, biodiversity and restoration targets, based on current funding commitments, likely policy implementation and market trends.
Figure 7 provides an overview of some of the key findings. US$7 trillion per year in naturenegative finance flows vastly overshadow efforts to increase finance for NbS, which is currently at US$200 billion per year. Finance flows to NbS are also much smaller than investment needs and opportunities, which call for the tripling of NbS finance by 2030 to meet Rio targets. The next section focuses on high-level recommended actions to put us on a pathway to a nature and climate positive future, for which investing in NbS is essential.
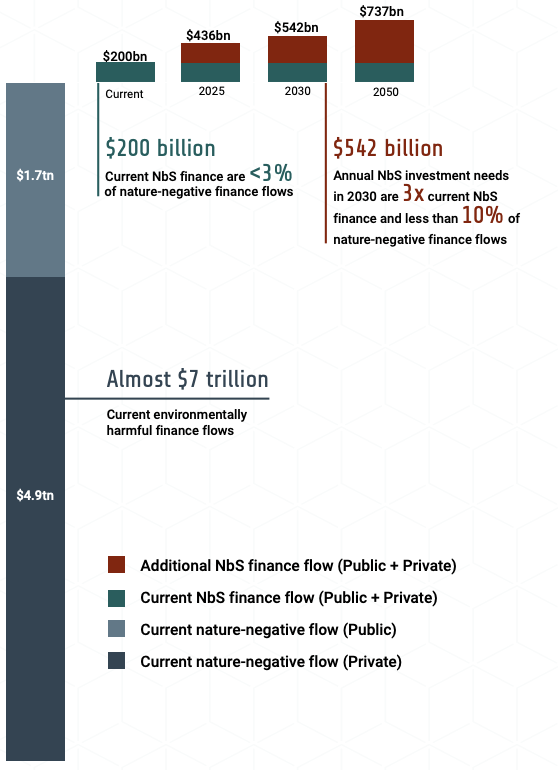
Figure 7. Current finance flows to NbS, nature-negative finance and investment needs
Recommendations for action
Building on SFN 2022, recommendations focus on:
- Greening finance – Reducing public and private nature-negative finance flows
- Financing green – Scaling public funding and private investment into NbS
- Green and inclusive financial systems – Ensuring a just transition to a green and inclusive financial system for vulnerable groups, women and Indigenous Peoples
Greening finance - eliminating nature-negative finance
Tackling nature-negative finance flows is the single most impactful intervention that can be made in the nature-climate space. Much of the funding required for NbS deployment can be realised in this way whilst at the same time ensuring a just transition.
Private nature-negative finance
The US$5 trillion invested in nature harming activities by the private sector each year must be realigned to become climate- and nature-positive. Essential actions for business and finance include:
- Assess, report and disclose nature risks, impacts, dependencies and opportunities using available disclosure frameworks, e.g. The Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD).
- Commit to targets reducing biodiversity and climate impacts using available guidance and tools, e.g. Science Based Targets Network (SBTN).
Public nature-negative finance
Governments must reform and repurpose the US$1.7 trillion spent on ineffective and inequitable environmentally harmful subsidies every year. This repurposing can free up large volumes of finance for NbS with no additional budgetary outlays.
Public provision of the enabling environment for private action
Governments must encourage and consider mandating assessment, reporting and disclosure of nature risks, impacts, dependencies and opportunities by business and finance. Increased use of regulation and incentive mechanisms are critical tools for governments to shape private sector action and behaviour.
Financing green - scaling public funding and private investment into NbS
Public finance for NbS
- Embed biodiversity, restoration and climate targets in law with targets on finance. Real change will require countries to embed targets in law and put in place strategies for implementation.
- Governments must continue to lead on funding and spending on NbS and should increase domestic expenditure on NbS, particularly NbS providing public goods.
- Increase ODA and NbS share of ODA. Given much of the responsibility for climate change, biodiversity loss and land degradation lie with the developed countries and given much of remaining biodiversity and nature-based carbon stores are located and under threat in developing countries, there is a strong case for scaling up concessional and grant development finance to developing countries.
Government action to catalyse private finance for NbS
Government policies play a key role in creating an enabling environment for the private sector to invest in NbS.
- Government regulation can be a powerful tool when private sector action is critical. Regulation that would make biodiversity offsetting mandatory has driven private sector investment in actions to conserve and restore biodiversity in many countries
- Government provision of incentives for investment in NbS needs to be scaled.
- Governments can incentivise private investment by reducing the costs and/or risks for private entities through blended finance instruments.
- Other key tools for government to catalyse private investment in NbS include supporting the development of high integrity nature markets and mandatory compliance by the private sector as well as developing green, sustainable and/or NbS taxonomies.
Scaling private NbS finance
Businesses and financial institutions need to to increase investment in Nbs and transform economies to nature- and climate-positive. There exists now a critical mass of knowledge and experience of a range of mechanisms to support scaling private finance for NbS, including prioritising investment in sustainable supply chains and in high-integrity nature markets and expanding the use of innovative green financial instruments (e.g. conservation or sustainable bonds and green insurance products). NbS may be developed as an asset class in a wider portfolio of nature assets.
Ensuring a just transition to a green and inclusive financial system for vulnerable groups, women and Indigenous Peoples
There are real inclusion and human rights challenges with the current approaches to incentivising conservation and restoration of nature.
- The expansion of protected areas and other NbS needs to take account of human rights and be based on best practice and apply the highest standards and environmental and social safeguards.
- The scale up of NbS finance in line with Rio targets needs to include finance for activities that enhance the role of Indigenous Peoples in the management of biodiversity and ecosystems.
- Governments need to lead. In addition to providing the legal and policy frameworks, public money can be used as blended and concessional finance to support development of Indigenous Peoples and women led nature-based enterprise.
- Nature markets and other innovative financial instruments need to be developed to work more justly and efficiently in favour of Indigenous Peoples and other marginalised groups including women who successfully steward nature, often facing serious challenges.
Concluding remarks
This report provides policy makers, businesses and financial institutions with an evidence-based snapshot of the very large scale of nature-negative finance flows, which at almost US$7 trillion per year dwarfs finance flows to NbS of US$200 billion per year. Urgent action to tackle nature-negative flows is critical. Unless the real economy and financial system reduce the financing of naturenegative activities (“greening finance”), actions to scale up investment in NbS (“financing green”) will be insufficient to reach Rio targets and transform the economic system to be more nature-positive and equitable.
Nevertheless, investing in NbS enables the use of nature’s potential to help cost-effectively tackle climate change, biodiversity loss and land degradation. Current investment is far from what is needed. Tripling NbS finance flows to US$542 billion by 2030 can make a massive contribution to reach Rio targets. The solution requires a new dual approach scaling up public and private investment into NbS whilst reducing nature-negative finance flows from both public and private sources.
The first requirement is to continue to upscale investment into NbS for climate and nature conservation and restoration. This is often the only tangible funding available to directly stem the tide of nature’s loss and to protect, maintain and restore vital ecosystems. This report documents the huge opportunities for impact by investing in protection, sustainable land management and restoration. The science, evidence, frameworks and policy tools as well as financial innovation are well-developed. What is needed now is implementation by governments, businesses and financial institutions.
Second, greater emphasis is needed to create incentives to realign finance away from naturenegative activities and towards creating naturepositive outcomes. Investment opportunities in NbS are increasing through the transformation of the global food system, extractive sectors, real estate and infrastructure, sectors that are mostly closely linked to nature’s loss. These opportunities will be at least as large as those that have emerged in response to the climate crisis.


